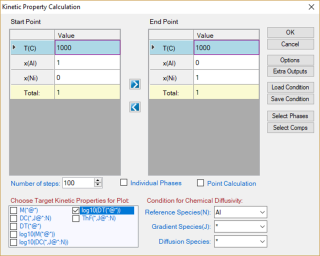
Kinetic Property
Diffusivity related properties can be calculated from Pandat™ as long as the corresponding species mobility parameters are available in the database. User can input the calculation condition through the interface shown in Figure 1 and select the desired properties for output. The default graph is the selected property as shown in Figure 2. If two or more properties are selected, they will be plotted separately.
Details on the kinetic models for the multicomponent diffusion are referred to the literature [1982Ågr, 1992And]. Only the key equations related to the properties of mobility, tracer diffusivity and chemical diffusivity are given in the below sections.
Atomic Mobility
In order to simulate diffusivity related properties such as chemical diffusivities of components, atomic mobility data of species in phases are required and stored in the database. Mobility of species k is related to its activation energy (Qk) by
|
|
(1) |
where is a frequency factor, R is the gas constant and T the temperature in Kelvin. Define MQk as
|
|
(2) |
Then, atomic mobility can be calculated from MQk. MQk is a function of composition, temperature and pressure and can be expressed as Redlich-Kister type of polynomial expansion as for the excess Gibbs energy [1982Ågr]. Each polynomial coefficient is stored in database. For example, the coefficient for term contributed to Al from Ni in Fcc phase () is described in TDB file as follows,
Parameter MQ(Fcc&Al,Ni;0) 298.15 -285517+R*T*Ln(0.0007933); 6000 N !
In Pandat™, atomic mobility of species can be obtained through table operation with field of “M(*@*)”. For example, M(Al@Fcc) represents the atomic mobility of Al in Fcc phase.
Tracer Diffusivity
Tracer diffusivity of a species k is directly related to its atomic mobility by
|
|
(3) |
where R is the gas constant and T the temperature. Tracer diffusivity can be obtained in Pandat™ from table with field of DT(*@*). For example, the tracer diffusivity of Al in Fcc can be extracted from calculation result with the table field of DT(Al@Fcc). The natural logarithm of the tracer diffusivity is available with logDT(*@*).
Chemical Diffusivity
Chemical diffusivity of species k, , could be calculated by
|
|
(4) |
|
|
(5) |
And
|
|
(6) |
where S represents the set of the substitutional species, dik is the Kronecker delta, and mi is the chemical potential of species i. uk is defined as
|
|
(7) |
Chemical diffusivity of species k in phase p can be obtained in Pandat™ with the table field of DC(k,j@p:n), where j and n are the gradient species and the reference species, respectively. Its corresponding natural logarithm is logDC(k,j@p:n).